M4 Origination Points
Origination Point is a connection from some initial entity (device/line/trunk/provider/supplier/etc) where the call starts/originates.
The call comes from Origination Point and goes to Termination Points.
Timeouts
- Progress Timeout – allows limiting the maximum time we will wait before we get media (whether it's early media (SIP 183), ringing (SIP 180), or answer (SIP 200)). If set to 0, then default progress timeout will be used which is 3 seconds.
- Ringing Timeout - allows limiting ringing duration (in seconds). Leave 0 for unlimited.
- Call Timeout - allows limiting Call duration (in seconds). Leave 0 for unlimited (global Call timeout (7200 seconds) is still applicable in this case).
Authentication Simple
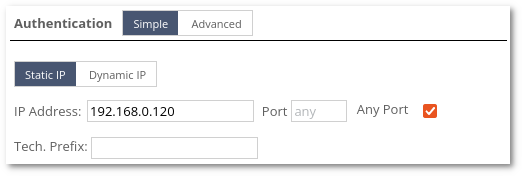
Static IP:
- IP Address - IP address of Origination Point (subnetting and IP range are allowed. For more information read the Subnetting and IP range sections below).
- Port - port of Origination Point.
- Tech. Prefix - Destination technical prefix that is used to authenticate OP. If this field is empty, calls will be accepted with any Destination number only based on IP:PORT. If this field is not empty, then only calls with specific prefixes in Destination will be authenticated (for example if Tech. Prefix is 00, then OP accepts Destination numbers that start with 00xxxxxxx).
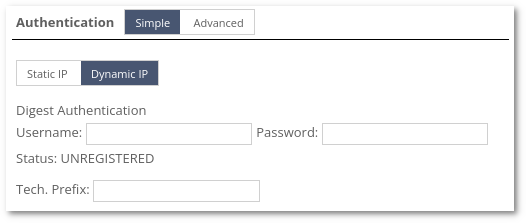
Dynamic IP:
- Username - the username you enter in your Device.
- Password - the password you enter in your Device.
- Status - registration status.
- UNREGISTER - by clicking this button, the last registration information will be deleted (IP, port).
- Tech. Prefix - Destination technical prefix that is used to authenticate OP.
Authentication Advanced
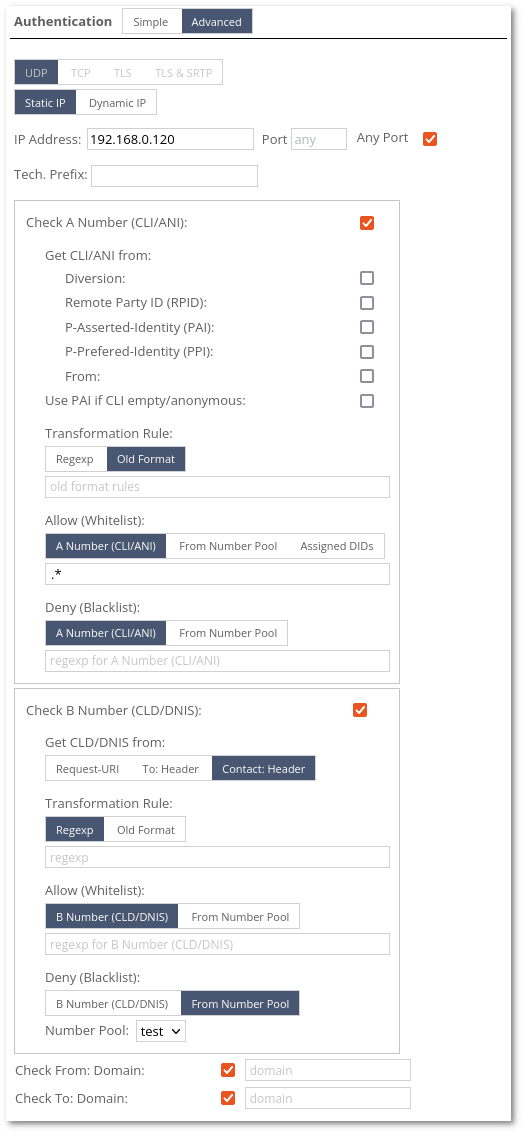
Static IP:
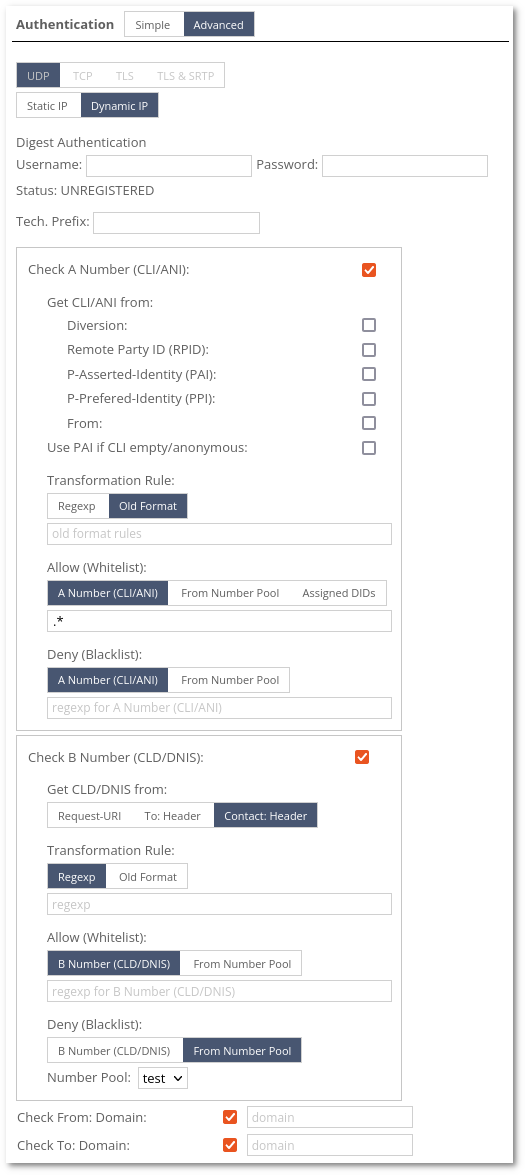
Dynamic IP:
Note: If several options from Get CLI/ANI from are selected, the system goes from the top and checks if there is a header until it finds it. Screenshot below.
Old Format transformation examples can be found here and here.
Regexp transformation examples can be found here.
Note: Allowed Transport allows enabling/disabling the transport type. One of the protocols must be enabled, in another case, the call would be rejected.
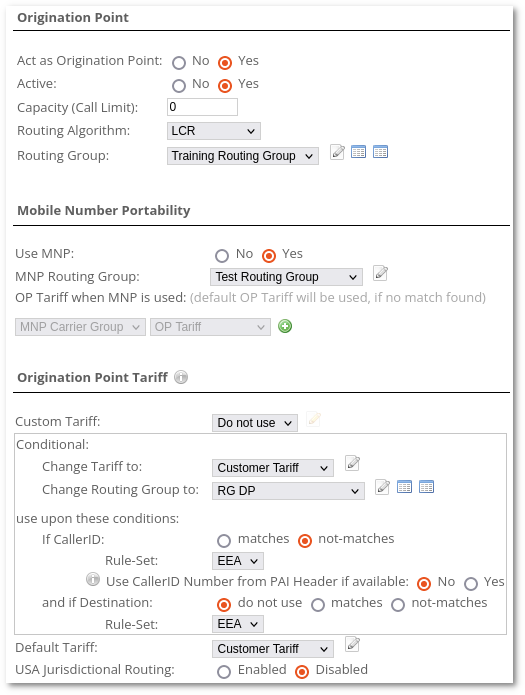
Origination Point
- Act as Origination Point - if set to 'yes', this Connection Point will be handled as Origination Point.
- Active - allows to activate or deactivate OP. If OP is deactivated, calls will not be accepted from this OP.
- Destination Transformation - special Destination Transformation rules used to modify outgoing number. Rules are applied before billing so they can be used to correct non-E164 formats.
- Source Transformation - special Source Transformation rules used to modify Source number.
- Routing Algorithm - defines how Termination Points are ordered for this Origination Point.
- Routing Group - Routing Group used for OP routing.
- Use MNP - enable MNP for this OP.
- MNP Routing Group - name of Routing Group used for MNP.
- OP Tariff when MNP is used - select OP Tariff when MNP is used. Default OP Tariff will be used if no match is found.
- Capacity - limit the number of concurrent calls for this OP (both ringing and answered calls are included in this limit).
- Source (CallerID) Allow - regular expression (regexp) that defines which CallerIDs are allowed to go through this OP. If you want to allow all CallerIDs, enter .* in this input field.
- Source (CallerID) Deny - regular expression (regexp) that defines which CallerIDs are denied to go through this OP.
- Custom Tariff - Custom Tariff that can override regular OP Tariff. If rates are found in Custom Tariff then these rates will be applied in accounting. If rates are not found in the Custom Tariff, then the regular OP Tariff is used.
- Conditional Tariff : XXXXX (description why and how to use it here)
Change Tariff and/or Routing Group if:
- CallerID matches/not matches Rule-Set: Number Pool Rule Set
- Use CallerID Number from PAI Header if available: No / Yes
- and if Destination: do not use/matches/not matches Rule-Set Number Pool Rule Set
- Using this option it is possible to use another tariff if CallerID and Destination matched Rule-Set. It is possible to create a Rule-Set at Maintenance - Number Pools. Also, it offers the possibility to use the CallerID Number from PAI Header if available.
- CallerID matches/not matches Rule-Set: Number Pool Rule Set
- Default Tariff - Tariff used for OP accounting if the previous option is not used.
- USA Jurisdictional Routing - Jurisdictional routing is telephone call routing logic based upon the locations of the calling and called the number and regulatory considerations. More information can be found here Here.
- M4: M4 configuration available here
CallerID
- Name - set name part for CallerID.
- Number - set number part for CallerID.
- Random Number from Number Pool - set random number from Number Pool. Only the number part for CallerID is set.
- Random - Send random CallerID from Number Pool.
- Pseudorandom with Deviation - Range can vary from 0 to 9999999. If 0 is chosen, then all numbers will be chosen the same amount of times. If 9999999 is set, then numbers will be completely random.
Codecs
The switch does not take into account the order of the codecs when the call comes from the Origination Point.
Codecs order are checked when the Origination Point is being dialed via DID. Defines which Codecs will be offered when dialing Originator (in the order they are listed).
Advanced
- Grace Time - if call duration is less than Grace Time, it will not be accounted for (CDR will be generated, but OP balance will not be reduced).
- Limit up to X Calls, during Y seconds - allows controlling Calls per Second (CPS).
Advanced Origination Point Settings
- Bypass Media - when set, the media (RTP) from the originating endpoint is sent directly to the destination endpoint and vice versa. The signaling (SIP) for both endpoints still goes through M4, but the media is point-to-point
- Use PAI Number for Routing - uses PAI Number instead of FROM callerID for routing.
- Send PAI Number as CallerID to TP - take a number from an incoming PAI header and use this number as CallerID for Termination Point.
- Forward RPID - by default forward RPID header from Originator to Terminator. This can be disabled by setting this option to "no". More info
- Forward PAI - by default forward PAI header from Originator to Terminator. This can be disabled by setting this option to "no". More info
- Change RPID/PAI Host - allows overwriting the original host address in RPID/PAI header with the proxy server's IP address.
- PAI Transformation - apply Transformation on PAI header. More info
- RPID Transformation - apply Transformation on RPID header. More info
- Disconnect Code Changes - allows changing hangup code which is returned to OP.
- Ignore SIP 183 without SDP - by default disabled. Select Yes to enable the option.
- Ignore SIP 180 after 183 - by default disabled. Select Yes to enable the option.
- Allow using own User's TPs - by default, it is not allowed to route the call through TP which belongs to the same User. Such a call results in HGC 339. By setting this option to Yes, you can disable this protection.
- Add STIR/SHAKEN Identity – should we add the SIP Identity header when calling from this Origination Point? More info on STIR/SHAKEN.
- STIR/SHAKEN Attestation Level – set attestation level. By TP, A, B, C, or Default (use stirshaken_attest_level from /etc/m2/system.conf). More info on STIR/SHAKEN.
- Fix NAT'ed Contact – When this setting is enabled, M4 replaces the local IP in the Contact header with the source IP.
Subnetting
It is possible to set subnetwork (subnet) for Origination Point. Subnets allow you to have a single Origination Point for multiple IP addresses. Instead of IP address, you can set subnet in IP Address input field. Subnet should be written in CIDR notation (for example 192.168.0.1/28). When a subnet is used in Origination Point, all calls coming from that subnet will be authenticated.
M4 subnet value range is 4-30.
You can use an online subnet calculator to check IP addresses for a given subnet.
IP range
If you need to set multiple IP addresses for a single Origination Point and Subnetting does not meet your needs, then you can set IP ranges. Ranges are written in the following format:
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx-yyy
When an IP range is used in Origination Point, all calls coming from that IP range will be authenticated. For example, if we have an IP range 192.168.0.101-150, then all IP addresses starting from 192.168.0.101 to 192.168.0.150 will be authenticated (50 different IP addresses are allowed to call to this Origination Point).