Number Manipulation
Number Manipulation is used to change Number formats.
Main RULES
MOR manipulates with numbers which are in E.164 format.
Explanation in other words: numbers coming to MOR SHOULD BE in E.164 format. Number leaving MOR ARE in E.164 format.
From this we come to necessary actions:
1. Incoming number should be made E.164 compatible (done by Localization)
2. Outgoing number should be made out of E.164 number (done by Provider Rules)
Definitions
- E.164 format - In short it's the number without international prefix which starts with country code, for more details - check Wikipedia.
- Localization
- Main idea of Localization: No matter how user dials number (destination) when localized it should be in e.164 format.
- Localization has nothing in common with numbers you send to providers. It operates with numbers received from caller.
- Provider Rules
- MOR operates with numbers in E164 format, but Provider often asks different format number - so Provider Rules formats E164 number to Provider acceptable format.
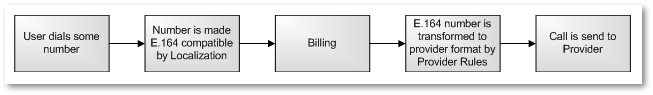
How Number Manipulation works
The first part which makes any incoming number E.164 compatible is done by Localization. The second one which changes E.164 number is Provider Rules. The basic schema for all this process can be simplified as:
MOR works only with E.164 numbers. That means, MOR accepts only standard numbers, if number is not in E164 - it must be changed to E164 compatible number.
For this task MOR has a feature "Localization" (found in Billing -> Functions -> Localization) which could be used for "standardizing non E.164 numbers to correct E.164 numbers".
If requested by outgoing calls provider, MOR can cut/add special prefix to number to send it to Provider in its requested format. This can be done using "Provider rules".
Localization and Provider Rules follows same logic.
Example how Localization works:
Number from Caller -> Localization -> Number from Caller in E164 format -> MOR -> Provider Rules -> Number for Calee
- International prefixes, local number formats are handled by Localization.
- Provider technical prefixes and special number formats for providers are handled by Provider Rules.
That means:
- if MOR receives number with international prefix – you need to strip it and make number E.164 compatible.
- if MOR received number in some local number format with some special digit(s) in front of it – you need to strip it, add country code -> make it E.164 compatible using Localization
- if your Provider requests some fancy technical prefix – you need to add this prefix using Provider Rules. Add prefix to E.164 number. It can occur that you need to cut some digits (let's say country code) before adding technical prefix – do it with Provider Rules.
Let's repeat again, because it is extremely important:
When MOR receives number – make sure it is E.164 compatible or make it E.164 compatible with Localization When you are sending number to provider – use Provider Rules to change E.164 number to provider expected format
Localization
Localization transforms received number to E.164 format number.
Main idea of Localization: No matter how user dials number (destination) when localized it should be in e.164 format.
Localization has nothing in common with numbers you send to providers. It operates with numbers received from caller.
Often it is important to let users to dial different format numbers to reach same destination. It depends on the location where user (or his device) is located.
For that purpose each device has field Location. It describes the physical location of device and rules how this device can dial destination. In other words – each device IS (belongs) in some Location where some specific dialing rules apply.
Location describes where caller IS - not where he is calling!
By default device has location 'Global'. Global rules apply to ALL devices. If user belongs to some other location and his dialed destination has some rule for his destination then global rules are not activated – they have lower priority upon location rules.
You can access Localization settings in SETTINGS – Billing – Functions – Localization.
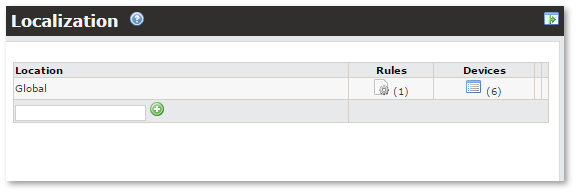
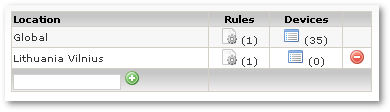
In the main window you can see available Locations:
At first there is only Global location. You can't delete this location. It's default for all devices.
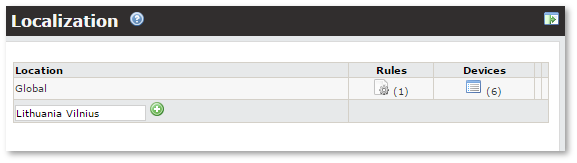
You can add new Location by entering this Location's name in field at the bottom of table:
In the column Rules press ![]() icon on to access Location's rules:
icon on to access Location's rules:
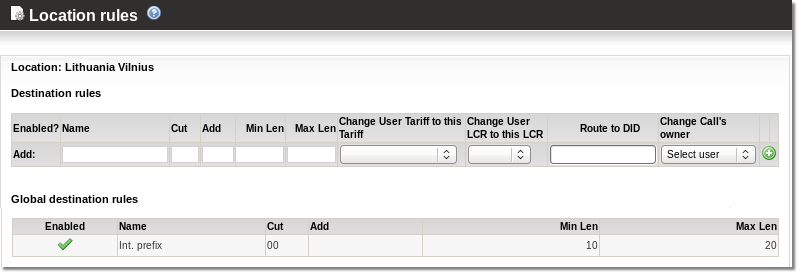
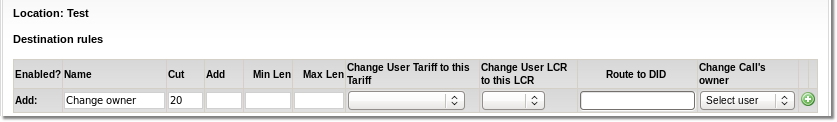
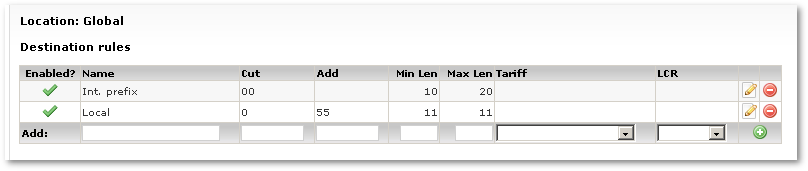
Following settings should be explained for rule:
- Name – just for informational purposes
- Cut – what prefix from the number should be cat
- Add – what prefix to the number should be added
- Min Len – what's the minimum length of number we are trying to apply this rule
- Max Len – what's the maximum length of number we are trying to apply this rule
- Tariff - which Tariff to apply when this Rule is applied. It is used in special cases, example here. Leave this empty in most cases
- LCR - which LCR to apply when this Rule is applied. It is used in special cases, example here. Leave this empty in most cases
When you enter all values (Cut or Add can be left empty – but just one of them at a time) press ![]() .
.
Example:
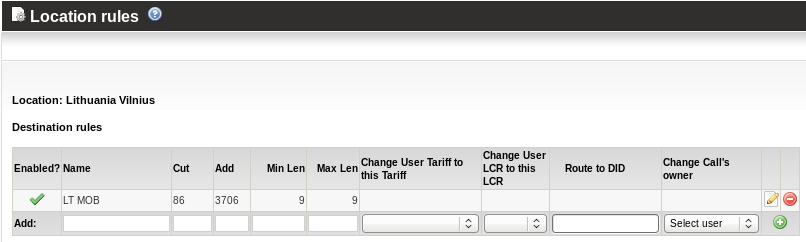
- Normal Lithuania MOB prefix is: 3706
- User's device is located in Lithuania Vilnius
- By current Lithuanian regulations local customer can dial 9 digit numbers starting with 86 to reach Mobile subscribers
To describe this situation we will create following rule:
Rules can be enabled or disabled pressing ![]() icon or
icon or ![]() accordingly in the Enabled? column.
accordingly in the Enabled? column.
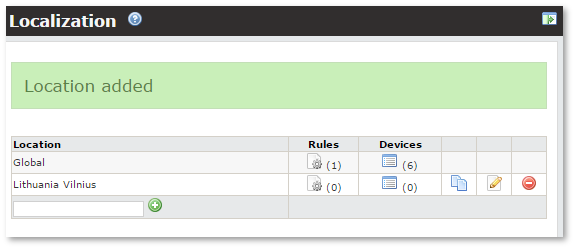
Now in the main Localization window:
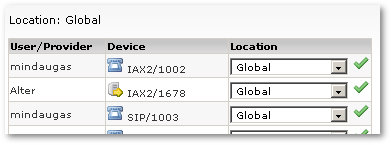
Press on ![]() in Devices column to access Devices in Global Location:
in Devices column to access Devices in Global Location:
Here all Devices with selected location are listed. Choose other location for selected Device and press on ![]() icon to activate this change. Device will be assigned to the selected Location.
icon to activate this change. Device will be assigned to the selected Location.
NOTE: It's possible to change Device's Location in Device's settings (SETTINGS – Users – Devices).
Now our device belongs to Location Lithuania Vilnius. And if we dial mobile number in Lithuanian format for example:
863042438, MOR cuts 86 (remaining part 3042438) and adds 3706. Result is: 37063042438 which is E.164 compatible and MOR can bill it correctly.
NOTE: make sure that after localization your number always is E.164 compatible. Call Tracing can help you do this.
Rule Ordering
Rules for Localization and for Provider Rules are ordered in following order:
- Device/Provider Location
- Global Location
That means that Global location rules are applied to every device. But they have lower priority over some specific Location. That means - if device belongs to some Location X, then rules in Location X are reviewed first. If none of the rules can be applied from Location X, then rules in Location Global are checked.
When one rule is applied - no more rules will be applied after that.
How exact rule for dialed number is selected from many rules
How MOR select rule which should be applied to the number?
There are 3 steps done for all rules (for Localization & Provider Rules)
1. MOR checks for number length and reject these rules if dialed Numbers length does not fall into MIN and MAX described interval. E.g. if Numbers length is less then MIN or greater then MAX.
2. Then these rules are rejected if beginning of number does not match Cut value of these rules.
3. At the last step MOR selects the rule which has longest Cut length.
E.g. Rule selected at step 3 will be used to transform dialed number.
Example
Lets say 012337068111543 coming from caller to MOR system.
And we have such rules:
# CUT ADD MIN MAX 1 01 11 11 14 2 012 22 12 15 3 123 33 15 16 4 0123 44 11 20
1. MOR is checking number length by available min/max settings. So if incoming number's length (number length = 15 in our example) is more or equal then MIN and less or equal then MAX - this rule will not be rejected. E.g. rule will be rejected if number length will be less then MIN or greater then MAX.
Then we are rejecting rule #1 because 15 is > MAX(14), after first step we have:
# CUT ADD MIN MAX 2 012 22 12 15 3 123 33 15 16 4 0123 44 11 20
2. MOR proceeds to looks for CUT value which match beginning of dialed number. MOR rejects all rules which do not match dialed number beginning.
In this step we are rejecting rule #2, because its CUT value (123) is NOT beginning of dialed number: 012337068111543.
After second step we have:
# CUT ADD MIN MAX 2 012 22 12 15 4 0123 44 11 20
3. MOR checks for all remaining rules which haven't been rejected by first and second rule and select rule which has longest CUT.
This step selects rule with longest CUT, so our result is:
# CUT ADD MIN MAX 4 0123 44 11 20
This rule is applied to dialed number. E.g. if dialed number is 012337068111543, then first we cut CUT value (0123) out from it (then we have 37068111543) and then we add ADD value (44), so final result is 4437068111543.
Example with Localization and Provider Rules for CallerID(Source) and Destination
Lets say 868555666 calling to 868777888, the first number is source (CallerID) and another one is destination. Localization source rules is used to modify CallerID which comes to MOR and provider source rules is used to modify CallerID which will be sent to provider. They aren't used all the time, only when owner of system wants.
So for example provider accepting calls only in 9 number length and which begins with 8. MOR works only with E.164 startard callerID's if you want to run billing on them.
So first of all we'll need to make such localization source rule for our situation:
Cut: 8 , Add: 370 , Min/Max 9/9.
So now callers number is 3708555666, not 868555666. MOR identifies caller from Lithuania (by country code 370), that means he can bill him.
Now we need to send a call to 868777888 , but our number must be in old format (868555666), so we need to apply such provider source rule:
Cut: 370, Add: 8 , Min/Max 11/11
Thats it, final caller's number will be 868555666 again.
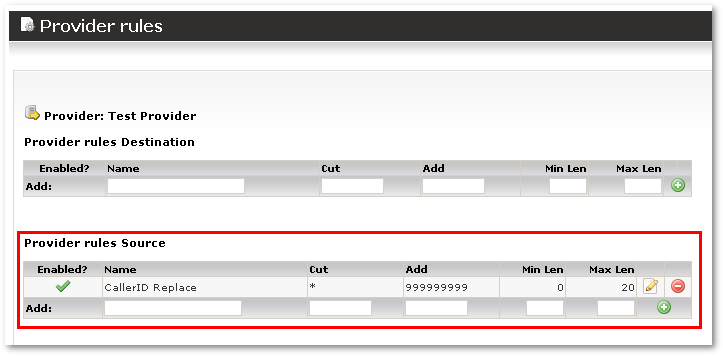
CallerID overwrite for Provider
(This functionality active from app_mor.so v0.7.41)
Sometimes Providers only accepts calls only with some CallerID.
It is possible to overwrite any CallerID before sending call to such Provider.
In Provider Rules (for this Provider) setup such Rule:
In this example all calls going to this Provider will have CallerID = 9999999999
Examples
Example 1 -  Italy
Italy
Client has such situation:
My customers are mainly in Italy. To call to Italy they are not gonna put 0039 country code, while they do put 00 and country code when the want to call other countries.
Then, on the other side, my provider aspect numbers to Italy without 0039 country code, while to other countries they do aspect it before the called number.
NOTES:
- Numbers clients dial are 10 digits in length. More info about Italian number format: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%2B39
- '+' is not used, it should be changed to '00'
To handle such situation such actions should be taken:
- Location 'Italy' should be created
- All devices from Italy should be assigned to this Location
- Rules in Location Italy:
- Name: 'Local Italy', Cut: (empty), Add: 39, Min: 6, Max: 10
- Name: 'International', Cut: 00, Add: (empty), Min: 11, Max: 16
- Provider Rules for Provider through which call will be terminated:
- Name: 'International', Cut: (empty), Add: 00, Min: 10, Max: 100
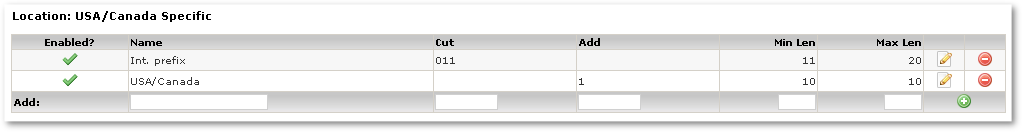
Example 2 -  USA/
USA/ Canada
Canada
Client has such situation:
- Local number is dialed in following formats: 1-XXX-XXX-XXXX or XXX-XXX-XXXX
- International numbers: 011 - country code - area code - number
Localization rules:
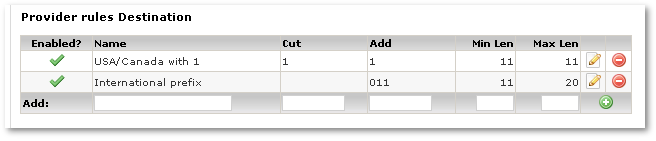
Now call should be sent to Provider which accepts number in following format:
- USA/Canada calls should start with 1
- International calls should start with 011
Provider rules for this Provider should look like:
Example 3 -  Brasil
Brasil
- Local number dialed in format 0XXXXXXXXXX
- International: 00 + country code + area code + number
See also: