Difference between revisions of "M4 Connection Points"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
[[File:m2_connection_point_create.png]] | [[File:m2_connection_point_create.png]] | ||
To create a new Connection Point, press on the "ADD NEW CONNECTION POINT" button. | To create a new Connection Point, press on the "ADD NEW CONNECTION POINT" button. | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 22 September 2020
Creating a Connection Point
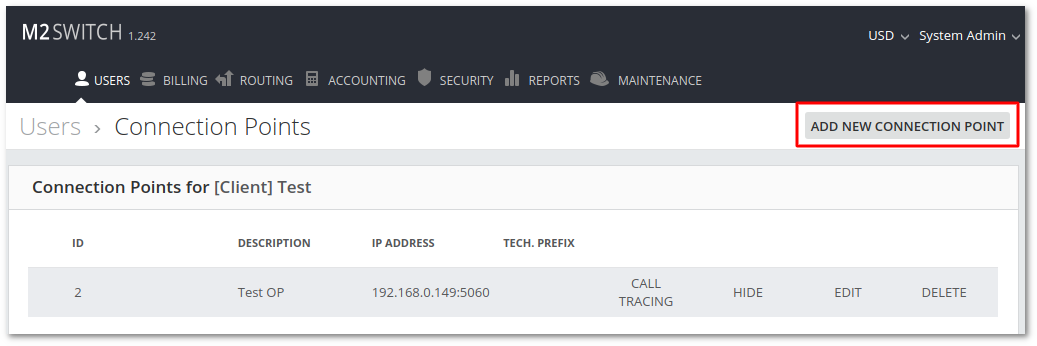
Go to User's list menu in USERS -> Users and press on the Device icon ![]() . The new page will show a list of Connections Points for that User (if any are available).
. The new page will show a list of Connections Points for that User (if any are available).
To create a new Connection Point, press on the "ADD NEW CONNECTION POINT" button.
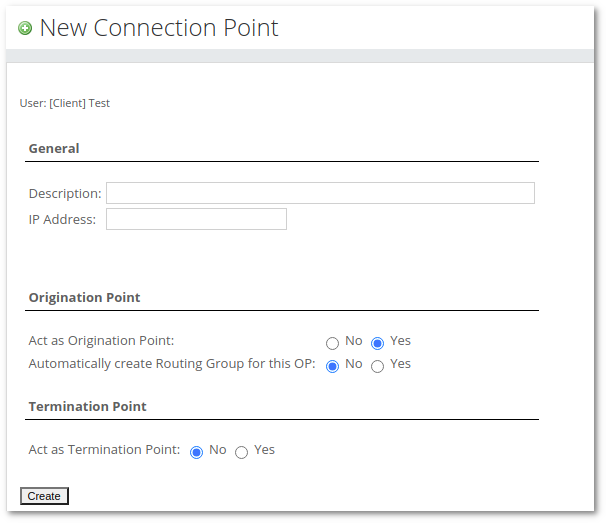
A new window will appear, there you can select general Connection Point Settings.
- Description – Description of Connection Point for informational purposes.
- IP Address - IP Address of Origination Point ( subnetting and IP range is allowed).
- Act as Origination Point - if set to 'yes', this Connection Point will be handled as Origination Point.
- Automatically create Routing Group for this OP - if set to 'yes', the system will automatically create a new Routing Group and will assign this new Routing Group in Origination Point settings.
- Act as Termination Point - if set to 'yes', this Connection Point will be handled as Termination Point.
Description:
General
- Accountcode – the unique ID of the device in the system.
- Description – for informational purposes.
- Type – what type of device it is.
- Ringing Timeout – allows to limit the ringing duration in seconds. Minimal value is 10 seconds.
- Call Timeout – allows to limit answered call billsec. Leave 0 for unlimited.
Servers
- Server – allows to choose server in multiple servers system.
Authentication
IP Authentication:
- IP Address – Device IP address (IP ranges and subnets are accepted).
- Port – Device Port.
- Dynamic IP – Allow Origination Point Authentication with Registration. More information here
Origination Point
All the information about these settings you can find – M2 Origination Points
Termination Point
All the information about these settings you can find – M2 Termination Points
CallerID
A CallerID consists of two parts: Name and Number. The "Number" part is transferred by default by all technologies (GSM, PSTN, SIP etc), but the "Name" part is transferred only by some. The number you see on your mobile phone when someone is calling you is the "Number" part.
- Name – the "Name" part of the CallerID.
- Number – the "Number" part of the CallerID. Only numerical values can be entered in this field.
NOTE: if you leave these fields empty, the user can set the CallerID name by himself. Usually it is not advisable to allow the user do it on his own. If CallerID number field is empty, system will take device username as CallerID number (if device is username/password authenticated).
- Random Number from Number Pool – This functionality gives you an ability to send different caller number on each Call. More information: Number Pool.
- Unknown - This option lets you set CallerID number to unknown.
Codecs
Choose the codecs your provider uses.
NOTES:
- If the Provider and the Device do not have similar codecs, no call can be established.
Advanced
- Grace Time - if call duration is less than Grace Time, it will not be accounted.
- Accept calls from any port – ignore the port number where request came from.
- Custom SIP Header - adds custom header to SIP request. Format is header: value (for example x-My-Custom-Header: my value)
- Limit up to (number) calls, during (number) seconds – allows to set calls per second limit in some period.

- Disconnect Code Changes – This functionality lets you to change one Hangup Cause Code into another. More information: Disconnect Code Changes.
- Ignore SIP 183 without SDP - SIP 183 (session progress) without SDP causes fake ring to be sent to originator. This setting allows to ignore SIP 183 without SDP and avoid fake ring.