Difference between revisions of "PBX connection to MOR"
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Here the main principles will be explained. For a detailed example, see the [[MOR and Trixbox | Trixbox]] section. | Here the main principles will be explained. For a detailed example, see the [[MOR and Trixbox | Trixbox]] section. | ||
In this diagram, one PBX is connected to the MOR | In this diagram, one PBX is connected to the MOR system. Two phones (Phone 1 and Phone 2) | ||
are connected to the PBX. Now both phones can dial out to the PSTN through PBX and MOR. | are connected to the PBX. Now both phones can dial out to the PSTN through PBX and MOR. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
This lets the user log in to GUI and see all incoming calls to his device. | This lets the user log in to GUI and see all incoming calls to his device. | ||
'''ATTENTION! In order for the virtual device to receive calls from the DID, the PBX should route calls to the correct device. MOR does not know the real location/connection type of the virtual device, it just sends the call to the PBX, and the PBX should send the call to the correct device. MOR CAN'T influence the PBX's configuration, so the PBX should be configured separately to handle incoming | '''ATTENTION! In order for the virtual device to receive calls from the DID, the PBX should route calls to the correct device. MOR does not know the real location/connection type of the virtual device, it just sends the call to the PBX, and the PBX should send the call to the correct device. MOR CAN'T influence the PBX's configuration, so the PBX should be configured separately to handle incoming calls from the DIDs.''' | ||
== | ==Examples== | ||
* [[MOR and Trixbox | MOR and Trixbox]]. | |||
* [[3CX_PBX_interconnection_with_MOR | MOR and 3CX]]. | |||
* [[3CX_PBX_interconnection_with_M4 | M4 and 3CX]]. | |||
Latest revision as of 11:37, 4 October 2023
Common connection diagram
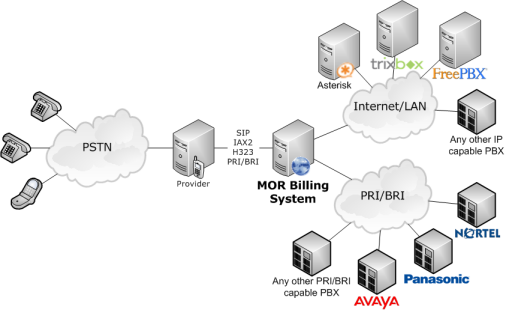
Any IP/PSTN-capable PBX can be connected to MOR:
To simplify the diagram, this is the common way for a PBX to be connected to MOR:
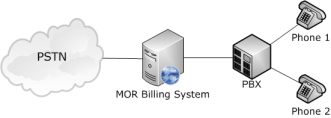
Here the main principles will be explained. For a detailed example, see the Trixbox section.
In this diagram, one PBX is connected to the MOR system. Two phones (Phone 1 and Phone 2) are connected to the PBX. Now both phones can dial out to the PSTN through PBX and MOR.
Dialing from PBX
Our task is to bill each phone separately.
- In MOR we need to create one User/Device for PBX.
- We need to create a Device for this PBX to describe how it is connected to MOR.
- You should mark this device as Trunk with ANI.
To bill our devices separately we need:
- To create one virtual device for each real device connected to PBX.
- In the device's CLI menu we need to add CallerIDs of these devices as described in PBX. Using the CallerID of the device, MOR recognizes who is calling and assigns the call to the correct device.
Dialing to PBX
DIDs should be forwarded to the PBX for a real device to get the call.
In order to assign a DID to a virtual device, the following steps are required:
- Mark the virtual device as Trunk.
- Assign a DID to the virtual device.
- Go to the device's Call Flow.
- In the Before Call state, forward the call to the PBX device.
That way, when a call goes to the virtual device through a DID, it should go through PBX Trunk.
If you do not forward the call to the PBX device, the call will fail.
This lets the user log in to GUI and see all incoming calls to his device.
ATTENTION! In order for the virtual device to receive calls from the DID, the PBX should route calls to the correct device. MOR does not know the real location/connection type of the virtual device, it just sends the call to the PBX, and the PBX should send the call to the correct device. MOR CAN'T influence the PBX's configuration, so the PBX should be configured separately to handle incoming calls from the DIDs.