WebRTC
WebRTC / WebSockets (WS/WSS)
WebRTC is supported from MOR X18 with PJSIP enabled.
Requirements
- Asterisk-20
- Rocky OS 9
- MOR X18 (or later)
- PJSIP enabled
- Domain in Asterisk server
- TLS (SSL) certificate
Enabling WebSockets
1. In Asterisk servers edit /etc/asterisk/http.conf and make sure that these settings are configured under [general] section:
[general] tlsenable=yes tlsbindaddr=0.0.0.0:8089 tlscertfile=/path/to/certificate tlsprivatekey=/path/to/private_key
Note: these settings should be already present in http.conf, but commented out. Just uncomment required settings.
Set proper path to TLS certificate in tlscertfile and private key in tlsprivatekey.
Example with Let's Encrypt. Generate certificates as in manual and set the proper path:
[general] tlsenable=yes tlsbindaddr=0.0.0.0:8089 tlscertfile=/etc/letsencrypt/live/your.domain.com/fullchain.pem tlsprivatekey=/etc/letsencrypt/live/your.domain.com/privkey.pem
2. Restart Asterisk:
systemctl restart asterisk
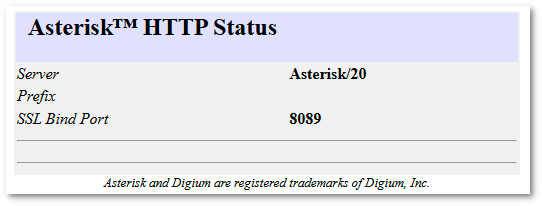
3. Check if Asterisk is accepting HTTP requests:
In browser, open the following address (with your own domain name):
https://YOUR_DOMAIN:8089/httpstatus
The output should be similar to this:
If this page is shown, Asterisk is configured to work with WebSockets protocol and WebRTC calls can be initiated using address:
https://YOUR_DOMAIN:8089/ws
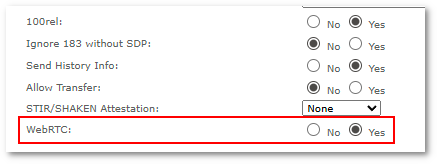
Enabling WebRTC in PJSIP Devices
Only PJSIP Devices are allowed to make WebRTC calls.
In PJSIP Device settings, enable WebRTC option under Advanced settings:
Tracing WebRTC calls
Since WebRTC calls are encrypted, it is difficult to capture calls directly using standard tools such as sngrep, wireshark, etc.
Asterisk allows to capture these calls using internal SIP logger by dumping UDP packets to PCAP file (even for encrypted calls) that can be later opened in sngrep or wireshark.
Enable SIP capture for all traffic
1. Run the following asterisk command to enable SIP logging:
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger on"
2. Save output to PCAP file:
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger pcap /root/asterisk_sip_capture.pcap"
3. When done, disable SIP logging:
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger off"
4. Open PCAP file inwireshark or in sngrep by specifying input file:
sngrep -I /root/asterisk_sip_capture.pcap
Enable SIP capture for specific IPs
1. Run the following asterisk command to enable SIP logging for specific IP:
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger host 192.168.0.111"
2. If needed, add additional IPs to capture (for example Provider IPs so that LegB side would be captured as well):
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger host 192.168.0.222 add"
Note the additional keyword add at the end.
3. Save output to PCAP file:
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger pcap /root/asterisk_sip_capture.pcap"
4. When done, disable SIP logging:
asterisk -rx "pjsip set logger off"
5. Open PCAP file in wireshark or in sngrep by specifying input file:
sngrep -I /root/asterisk_sip_capture.pcap
Testing with WebRTC Phone
To test if WebRTC / WebSockets are configured correctly, a Web Phone is required.
The following guide shows how to install Web Phone on your server for testing purposes.
1. Configure PJSIP Device with username/password in GUI and make sure WebRTC option is enabled under Advanced settings.
2. Download Browser Phone repository:
git clone https://github.com/InnovateAsterisk/Browser-Phone.git /usr/src/webrtc_phone
3. Install podman-docker engine, which we'll use to run the containerized NGINX (HTTP) server:
install podman podman-docker -y
4. Create directory for NGINX configuration:
mkdir -p /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl
5. Generate your test certificate and key (skip this step if you have proper TLS (SSL) certificate):
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/key.pem -out /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/cert.pem -days 365 -nodes -subj "/CN=localhost"
6. Create HTTP configuration for NGINX server:
echo -e "server {\n listen 443 ssl http2;\n server_name localhost;\n ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/cert.pem;\n ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/key.pem;\n location / {\n root /usr/share/nginx/html;\n index index.html;\n }\n}" > /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/nginx.conf
7. Run NGINX server (in this example, HTTPS port 8055 is used to access this Web Phone via browser):
podman run -d -p 8055:443 \ --name webrtc_phone \ -v /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:ro \ -v /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/cert.pem:/etc/nginx/ssl/cert.pem:ro \ -v /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/key.pem:/etc/nginx/ssl/key.pem:ro \ -v /usr/src/webrtc_phone/Phone:/usr/share/nginx/html \ docker.io/library/nginx
Note: if you used your own valid certificate and skipped step 4, then replace /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/cert.pem and /etc/webrtc_phone_ssl/key.pem in this command with paths to your certificate and key.
8. Check if Web Phone is accessible via address:
https://your.server.com:8055
Note: if you used self-signed certificate in step 4, then browser will complain about self-signed certificate. Most browsers still allow to access this page by pressing dedicated button (in Chrome and Edge, there should be ADVANCED button which allows you to continue to the web page).
If everything is correct, a license page should be loaded. Accept the license and configuration window should show up.
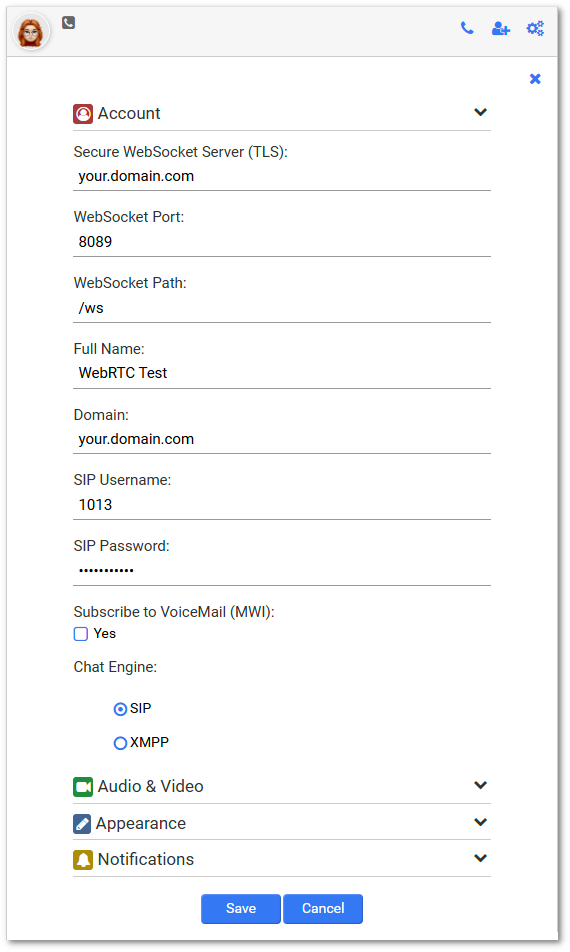
9. Configure Web Phone with the following settings:
Change your.domain.com to your Asterisk server domain and enter username/password of Device created in step 1. Make sure that WebSocket Port is set to 8089 and WebSocket Path is set to /ws.
Press Save to refresh window.
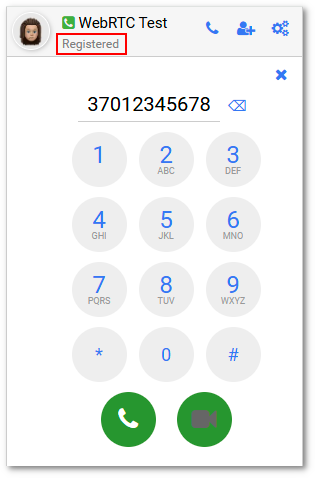
If registration is successful, you should see status in the upper left corner:
Try to make a WebRTC call.
10. If everything works correctly, you can stop Web Phone HTTP server:
podman stop webrtc_phone podman rm webrtc_phone
MOR X17 (or older) WebRTC/WebSockets/WSS
WebRTC together with MOR can be integrated using 3rd party solutions (Example: https://www.mizu-voip.com/Software/WebRTCtoSIP.aspx).
With Asterisk 1.8: Please note that only audio could work, because in our experience Asterisk 1.8 which MOR uses does not work properly with video over WebRTC.