MOR STIR/SHAKEN
About
MOR supports STIR/SHAKEN authentication (construction of the SIP Identity header).
Requirements
- Rocky 9 OS
- Latest Asterisk 20 (must be compiled after Mar 23, 2025)
- Latest MOR X18
- MOR Core 29.x.x
- PJSIP (STIR/SHAKEN works only with PJSIP Devices/Providers)
- Private key
- Public certificate (.pem file or URL to certificate)
Note: in MOR X18, PJSIP must be enabled by Kolmisoft support team.
Kolmisoft does not provide private key and public certificate. STIR/SHAKEN public certificate must be acquired from STIR/SHAKEN authorities.
Configuration
Global configuration
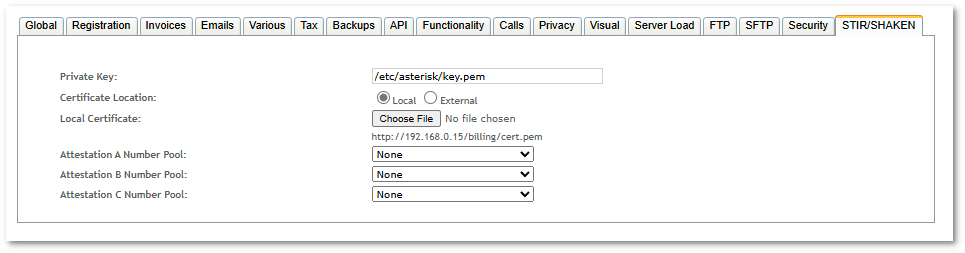
Global STIR/SHAKEN configuration is located in SETTINGS -> Setup -> STIR/SHAKEN.
- Private Key - path to private key which was used to acquire STIR/SHAKEN certificate. Private key must be located in this path in all Asterisk servers.
- Certificate Location
- Local - STIR/SHAKEN certificate will be uploaded and hosted in MOR server (GUI server). SIP Identity header will contain URL to certificate: YOUR_HOSTNAME/billing/cert.pem
- External - external STIR/SHAKEN certificate URL will be used to construct SIP Identity header.
- Attestation A Number Pool - number pool to use as list of A attested CLI numbers. Calls from these numbers will have SIP Identity header with A attestation level.
- Attestation B Number Pool - number pool to use as list of B attested CLI numbers. Calls from these numbers will have SIP Identity header with B attestation level.
- Attestation C Number Pool - number pool to use as list of C attested CLI numbers. Calls from these numbers will have SIP Identity header with C attestation level.
Note: wildcards are not supported in Attestation number pools. The only valid characters are the numbers 0-9, '#' and '*'.
Device/Provider configuration
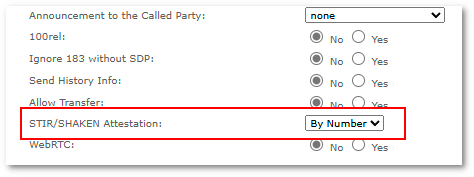
STIR/SHAKEN attestation can be enabled in Device or Provider Advanced settings:
- STIR/SHAKEN Attestation
- None - no STIR/SHAKEN attestation is performed.
- By Number - STIR/SHAKEN attestation will depend only on CLI numbers configured in global Attestation X Number Pool settings. All CLIs without a configured STIR/SHAKEN attestation level will be ignored - no SIP Identity header will be added (call will be routed normally).
- A, B, C - attestation level to use when CLI is not found in global Attestation X Number Pool.
Updating Certificate
STIR/SHAKEN certificates have an expiration date. When the new certificate is obtained, it must be either uploaded again to GUI server or external URL to this certificate updated.
Testing
To test STIR/SHAKEN functionality, you can create self-signed certificate. This certificate will not be accepted by any service provider, use it for testing only. In production environment, proper STIR/SHAKEN certificate must be obtained from STIR/SHAKEN Certificate Authorities by following their instructions.
Bellow are the steps to create self-signed STIR/SHAKEN certificate for testing purposes.
1. Login to Asterisk server.
2. Create directory for keys as certificate authority (CA):
mkdir /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-ca
3. Go to CA directory:
cd /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-ca
4. Generate private key using Elliptic-Curve cryptography:
openssl ecparam -noout -name prime256v1 -genkey -out ca-key.pem
5. Generate certificate (public key). When asked for input, just press ENTER to skip filling details:
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca-key.pem -sha256 -days 1825 -out ca-cert.pem
6. Create directory for keys as service provider (SP):
mkdir /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-sp
7. Go to SP directory:
cd /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-sp
8. Generate private key:
openssl ecparam -noout -name prime256v1 -genkey -out sp-key.pem
9. Generate TNAuthList:
cat > TNAuthList.conf << EOF asn1=SEQUENCE:tn_auth_list [tn_auth_list] field1=EXP:0,IA5:1001 EOF
10. Generate .der file:
openssl asn1parse -genconf TNAuthList.conf -out TNAuthList.der
11. Generate openssl.conf:
cat > openssl.conf << EOF [ req ] distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name req_extensions = v3_req [ req_distinguished_name ] commonName = "SHAKEN" [ v3_req ] EOF
12. Append hex-encoded TNAuthList to openssl.conf:
od -An -t x1 -w TNAuthList.der | sed -e 's/ /:/g' -e 's/^/1.3.6.1.5.5.7.1.26=DER/' >> openssl.conf
13. Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), which we will finally "submit" to our Certification Authority (CA):
openssl req -new -nodes -key sp-key.pem -keyform PEM -subj '/C=US/ST=VA/L=Somewhere/O=MOR, Inc./OU=VOIP/CN=SHAKEN' -sha256 -config openssl.conf -out sp-csr.pem
14. As the Certification Authority (CA), we accept the CSR, then generate and sign the STIR/SHAKEN certificate:
openssl x509 -req -in sp-csr.pem -CA /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-ca/ca-cert.pem -CAkey /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-ca/ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -days 825 -sha256 -extfile openssl.conf -extensions v3_req -out sp-cert.pem
15. Copy certificate to GUI server's public directory /home/mor/public with the name cert.pem (or transfer via FTP if GUI is in another server):
cp -f /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-sp/sp-cert.pem /home/mor/public/cert.pem
16. Set private key /etc/asterisk/stir-shaken-sp/sp-key.pem in GUI Global STIR/SHAKEN settings and make sure "Certificate location" is set to "Local".
17. If needed, configure Attestation Number Pools.
18. In PJSIP Provider settings, set STIR/SHAKEN Attestation to "By Number" / "A" / "B" / "C", depending on your scenario.
19. Make a call to this Provider and using sngrep (or any other packet tracer), check the outgoing SIP INVITE, you should see SIP Identity header similar to this:
Identity: eyJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiIsInBwdCI6InNoYWtlbiIsInR5cCI6InBhc3Nwb3J0IiwieDV1IjoiaHR0cDovLzE5Mi4xNjguMC4xNS9iaWxsaW5nL2NlcnQucGVtIn0.eyJhdHRlc3QiOiJDIiwiZGVzdCI6eyJ0biI6WyIzNzAxMjM0NTY3OCJdfSwiaWF0IjoxNzUwNDU2MzcxLCJvcmlnIjp7InRuIjoiMzcwMDAwMDAwMDAifSwib3JpZ2lkIjoiZDVjNDFmNzMtYjZjZC00MmUzLTlkMDYtYzZmZTIxM2ZiMDdiIn0.z0Cj_0_yrSkPc55q7HEhIZrrNCidckF69Tn9gpLdntQsCJ6AW1T-bpI88lAfRC4-ItnV7MZkw8BJyewUdy52ag;info=<http://192.168.0.15/billing/cert.pem>;alg=ES256;ppt=shaken
The most important part is JWT token:
eyJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiIsInBwdCI6InNoYWtlbiIsInR5cCI6InBhc3Nwb3J0IiwieDV1IjoiaHR0cDovLzE5Mi4xNjguMC4xNS9iaWxsaW5nL2NlcnQucGVtIn0.eyJhdHRlc3QiOiJDIiwiZGVzdCI6eyJ0biI6WyIzNzAxMjM0NTY3OCJdfSwiaWF0IjoxNzUwNDU2MzcxLCJvcmlnIjp7InRuIjoiMzcwMDAwMDAwMDAifSwib3JpZ2lkIjoiZDVjNDFmNzMtYjZjZC00MmUzLTlkMDYtYzZmZTIxM2ZiMDdiIn0.z0Cj_0_yrSkPc55q7HEhIZrrNCidckF69Tn9gpLdntQsCJ6AW1T-bpI88lAfRC4-ItnV7MZkw8BJyewUdy52ag
It consists of three base64url-encoded parts separated by a dot:
header.payload.signature
Copy this JWT token to any online JWT decoder to see its contents:
Decoded header
{
"alg": "ES256",
"ppt": "shaken",
"typ": "passport",
"x5u": "http://192.168.0.15/billing/cert.pem"
}
Decoded payload
{
"attest": "C",
"dest": {
"tn": [
"37012345678"
]
},
"iat": 1750456371,
"orig": {
"tn": "37000000000"
},
"origid": "d5c41f73-b6cd-42e3-9d06-c6fe213fb07b"
}
In the payload, we can see that source number 37000000000 to destination number 37012345678 was attested with C level.
Decoded signature is omitted from this example.