Difference between revisions of "M4 PAI And RPID Header Generation"
From Kolmisoft Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
(Created page with "M4 can generate P-Asserted-Identity (PAI) and Remote-Party-ID (RPID) headers =Usage= Go to '''Users -> Connection Points''', click EDIT on Connection Point. PAI/RPID Transformations are located under '''Termination Point Signaling Settings'''. File:Rpid_pai_to_tp_generation.png Generation can happen under '''Generate if missing''' and '''Overwrite''' tabs. =Generation format= Generation string should be either: * a static string (the value of the RPID/PAI heade...") |
Tag: Manual revert |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=Examples= | =Examples= | ||
sip:3701234567@myhost.sip - simple static generation. | <sip:3701234567@myhost.sip> - simple static generation. | ||
sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid - simple static generation. | <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid> - simple static generation. | ||
sip:$fU@myhost.sip - using Kamailio variable $fU to generate header with value from SIP FROM header | <sip:$fU@myhost.sip> - using Kamailio variable $fU to generate a header with the original value from SIP FROM header | ||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
* [[ | * [[M4 RPID/PAI]] Forwarding/Host changing | ||
* [[ | * [[M4 Origination Points]] | ||
* [[ | * [[M4 Termination Points]] | ||
* [[M4 Transformations]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:21, 18 December 2025
M4 can generate P-Asserted-Identity (PAI) and Remote-Party-ID (RPID) headers
Usage
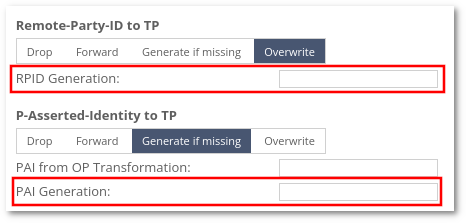
Go to Users -> Connection Points, click EDIT on Connection Point. PAI/RPID Transformations are located under Termination Point Signaling Settings.
Generation can happen under Generate if missing and Overwrite tabs.
Generation format
Generation string should be either:
- a static string (the value of the RPID/PAI header)
- a string mixed with Kamailio variables
Examples
<sip:3701234567@myhost.sip> - simple static generation. <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid> - simple static generation. <sip:$fU@myhost.sip> - using Kamailio variable $fU to generate a header with the original value from SIP FROM header
See also
- M4 RPID/PAI Forwarding/Host changing
- M4 Origination Points
- M4 Termination Points
- M4 Transformations