Difference between revisions of "M4 Kamailio Transformations"
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
= | =Special variables= | ||
In addition to Kamailio variable, system offer the following special variables: | In addition to Kamailio variable, system offer the following special variables: | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 20 February 2023
Kamailio transformations using regexp allow modifying PAI (P-Asserted-Identity) and RPID (Remote-Party-ID) headers.
Usage
Go to Users -> Connection Points, and click EDIT on Connection Point.
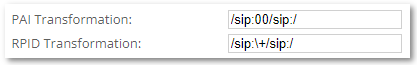
PAI/RPID Transformations for OP are located under Advanced Origination Point Settings:
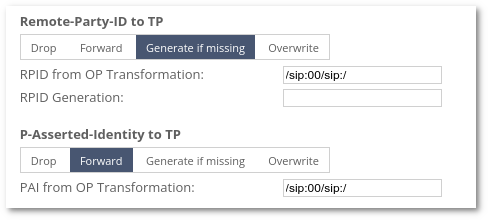
PAI/RPID Transformations for TP are located under Termination Point Signaling Settings:
Transformation format
/match_expression/replacement_expression/flags
- match_expression - POSIX regular expression
- replacement_expression - replacement expression with back references to matched tokes: \1, \2, …, \9
- flags:
- i - match ignore case
- g - replace all matches
Match Expression
POSIX regular expression (regex) matching is done on full PAI/RPID header (for example: "name" <sip:number@host>;params). This allows to match and modify any part of the header (name, number, host, parameters).
Replacement Expression
If the regex match is successful, then the portion which was matched is replaced with a replacement.
A Transformation:
/sip:00/sip:/
applied on a header:
<sip:00370123456789@example.sip>
would result in:
<sip:370123456789@example.sip>
Here we match sip:00 in the original header and replace it with sip:. If the original header did not contain a number starting with 00, then regex would not match and nothing is replaced.
Additionally, the replacement can contain \n (n is a number from 1 to 9, inclusive) references, which refer to the portion of the match which is contained between parentheses ( ). References are numbered by counting their opening parentheses from left to right.
A regex:
(.*) <sip:(.*)@(.*)>(.*)
applied on a header:
"John" <sip:00370123456789@example.sip>;user=phone
would produce the following references:
- \1 - "John"
- \2 - 00370123456789
- \3 - example.sip
- \4 - ;user=phone
Using these references you can construct your own header:
A Transformation:
/(.*) <sip:(.*)@(.*)>(.*)/\2 <sip:\2@myhost.sip>\4/
applied on a header:
"John" <sip:00370123456789@example.sip>;user=phone
would result in:
00370123456789 <sip:00370123456789@myhost.sip>;user=phone
Here we construct a new header and set the name part to \2 (which in our case is a number) and set static text as a host.
Kamailio variables
Replacement Expression accepts Kamailio variables.
As an example, let's replace the URI username (number part) in the PAI header with URI username from FROM header:
A Transformation:
/sip:(.*)@/sip:$fU@/
applied on a PAI header:
From: <1111111@myhost.sip> P-Asserted-Identity: <anonymous@myhost.sip>
would result in:
From: <1111111@myhost.sip> P-Asserted-Identity: <1111111@myhost.sip>
Here we are using the $fU Kamailio variable which refers to FROM URI username. PAI number anonymous is replaced with number 1111111.
Special variables
In addition to Kamailio variable, system offer the following special variables:
- $src - localized source number (number that will be sent to Termination Point)
Testing
Before putting Transformations to production, it is advisable to test them on various values.
Test in Linux console
Execute sed command (add s before transformation s/regex/replacement/flags):
echo '<sip:00370123456789@myhost.sip>' | sed -E 's/sip:00/sip:/'
Test in online sed live editor
If you do not have access to the Linux console, use https://sed.js.org/ (or any other online sed editor).
Validate regex
The Regex part of a Transformation can be validated using https://regexr.com/ (or any other online regex editor).
Quick notes
- Header must be present in order to apply Transformations
- In case of error, no changes will be applied
- Only POSIX regex is allowed
- If a Transformation was applied by OP settings, then TP Transformations will be applied on top of the already modified header
- Destination Transformation uses a different syntax, please refer to Destination Transformation
Examples
| Transformation | Original header | Modified header | Comment |
| /sip:00/sip:/ | <sip:003701234567@myhost.sip> | <sip:3701234567@myhost.sip> | Cut prefix 00 |
| /sip:\+/sip:/ | <sip:+3701234567@myhost.sip> | <sip:3701234567@myhost.sip> | Cut + (here + is escaped by \ since it is special regex symbol) |
| /sip:\+370/sip:86/ | <sip:+3701234567@myhost.sip> | <sip:861234567@myhost.sip> | Cut prefix +370, add prefix 86 |
| /sip:\+?(.*)/sip:+\1/ | <sip:3701234567@myhost.sip> | <sip:+3701234567@myhost.sip> | Add + if it is not present already |
| /sip:(.*)@/sip:$fU@/ | <sip:anonymous@myhost.sip> | <sip:3701234567@myhost.sip> | Using Kamailio variable $fU replace the original number with the number from SIP FROM header |
