P-Asserted-Identity
Description
The P-Asserted-Identity header field can be used to convey the proven identity of the originator of a request within a trusted network. Since the From header field is populated by the originating UA it may not necessarly contain the actual identity. It usually is established by means of authentication between the originating UA and its outgoing proxy. The outgoing proxy then adds a P-Asserted-Identity header field to assert the identity of the originator to other proxies.
This header field has only meaning within what is called a trusted network by mutual aggreement on the requirements for its use by the parties involved.
The P-Asserted-Identity header field is defined in RFC 3325.
Source: http://www.z9hg4bk.org/sip/hf/p-asserted-identity.html
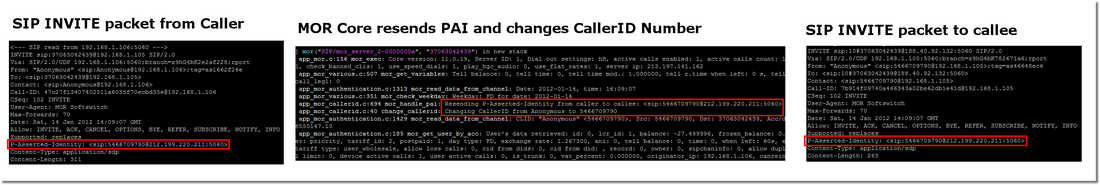
How P-Asserted-Identity (PAI) is handled in MOR
This functionality is available starting from MOR 11
- If caller sends PAI, MOR reads it and resends to the calee automatically
- If caller sends PAI and CallerID Number is 'Anonymous', MOR changes CallerID Number to the value from the PAI
- NOTE: CallerID Name is not changed! Only CallerID Number.
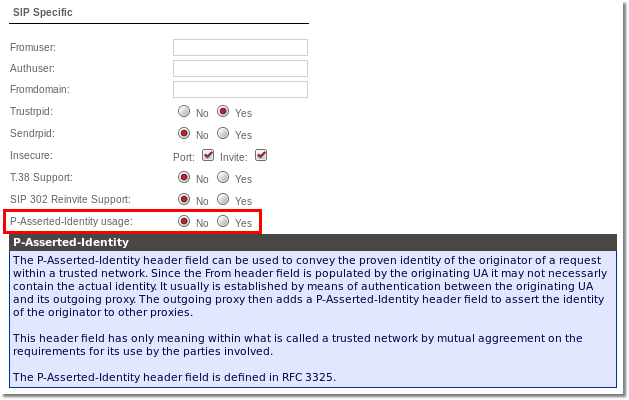
- If caller sends PAI and some Provider has P-Asserted-Identity usage enabled in it's Edit window, MOR ignores this setting, because it resends original PAI
- If caller is NOT sending PAI and some Provider has P-Asserted-Identity usage enabled in it's Edit window, MOR constructs PAI from CallerID, Server IP (from mor.conf file) and SIP Port (from sip.conf file).
Configuration for Provider to send PAI if it is not present from the Caller
This option is available starting from MOR 9
Turn it per Provider basis in its Settings:
mor.conf
Make sure correct external IP address is set in mor.conf in variable server_ip.