Difference between revisions of "LCR Logic"
From Kolmisoft Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
MOR first dials through Provider A. If the call fails, Provider B will be used to send the call. | MOR first dials through Provider A. If the call fails, Provider B will be used to send the call. | ||
If the call is ANSWERED, BUSY or there's NO ANSWER, the call ends, and Provider B is not used. | If the call through Provider A is ANSWERED, BUSY or there's NO ANSWER, the call ends, and Provider B is not used. | ||
Provider B is used ONLY when the call fails | Provider B is used ONLY when the call fails through CONGESTION. | ||
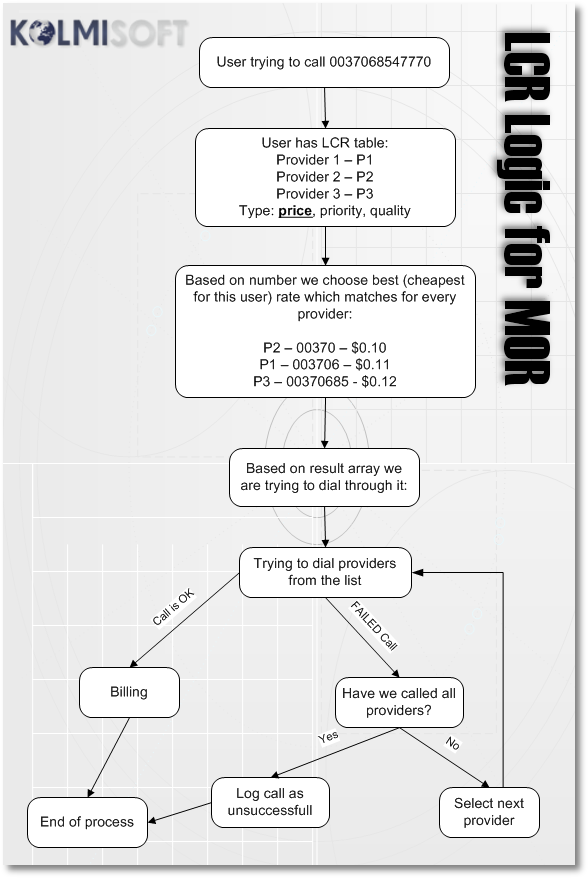
The following graphic illustrates LCR logic: | |||
[[Image:lcr_logic.png]] | [[Image:lcr_logic.png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:53, 15 May 2010
Here simple LCR (Least Cost Routing) is explained.
Example
We have two providers, A and B.
The dialed destination is 921XXXXXXXXXX.
Provider A has the following rate for the prefix (destination):
- 92 rate 0.1
No other destination starts with 92.
Provider B has the following rates for prefixes:
- 92 rate 0.05
- 921 rate 0.2
So LCR in MOR will group these providers in the following order:
- Provider A with rate 0.1 (92)
- Provider B with rate 0.2 (921)
MOR first dials through Provider A. If the call fails, Provider B will be used to send the call.
If the call through Provider A is ANSWERED, BUSY or there's NO ANSWER, the call ends, and Provider B is not used.
Provider B is used ONLY when the call fails through CONGESTION.
The following graphic illustrates LCR logic: