Difference between revisions of "Device settings"
(→Codecs) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:device_settings_sip.png]] | [[Image:device_settings_sip.png]] | ||
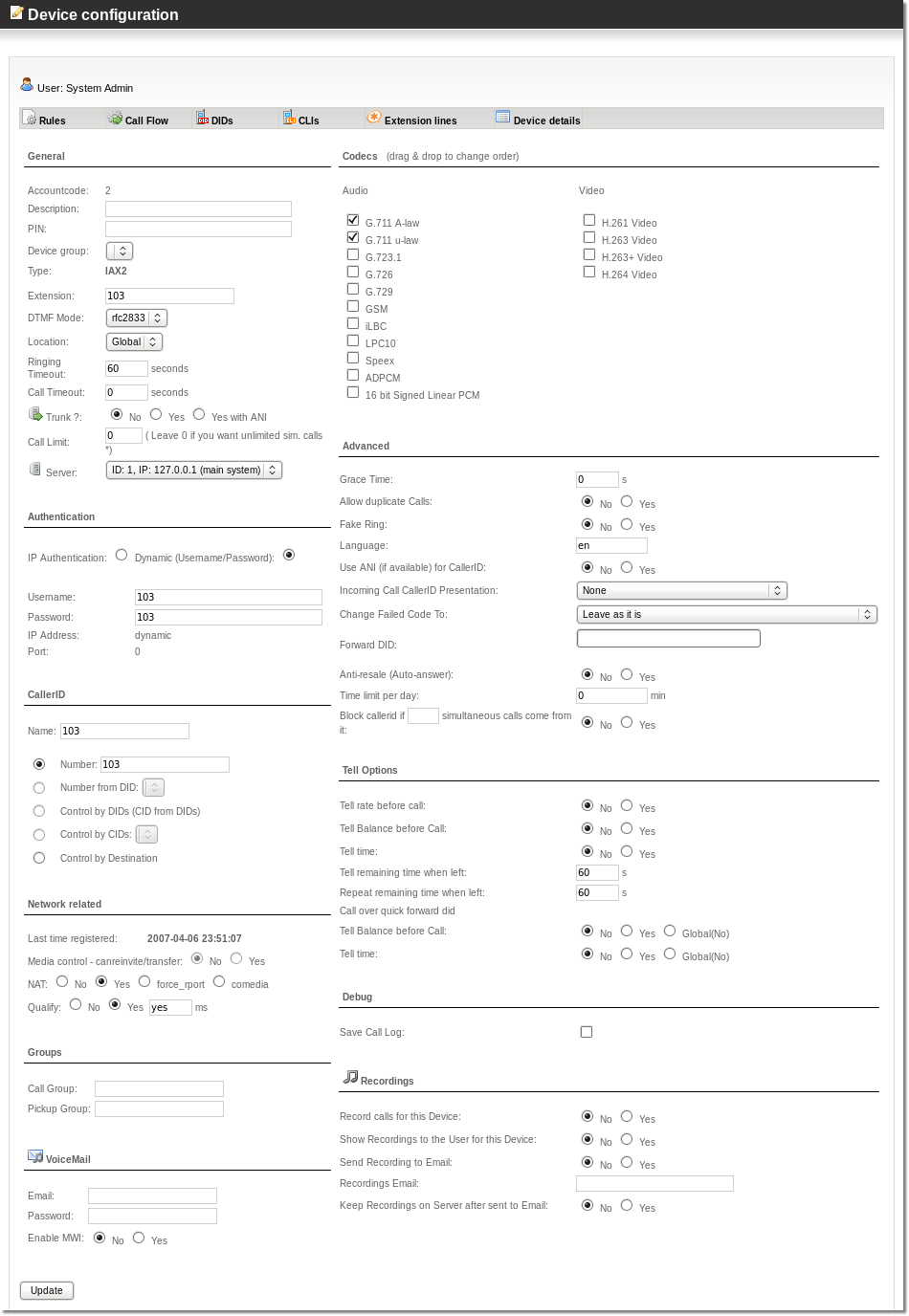
Each device can have many settings. | Each device can have many settings. The screenshot shows settings for an SIP device. These settings are similar to those for other device types also. | ||
There are several groups of settings: General, Authentication, CallerID, Network Related, Groups, Voicemail, Codecs, Allowed Addresses, Advanced, Tell Options, Debug and Recordings. | There are several groups of settings: General, Authentication, CallerID, Network Related, Groups, Voicemail, Codecs, Allowed Addresses, Advanced, Tell Options, Debug and Recordings. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=General= | =General= | ||
* '''Accountcode''' – unique | * '''Accountcode''' – the unique ID of the device in the system. | ||
* '''Description''' – for informational purposes | * '''Description''' – for informational purposes. | ||
* '''PIN''' – device PIN for authentication/authorization | * '''PIN''' – device PIN for authentication/authorization. | ||
* '''Device group''' - to which group device belongs (not used most of the time) | * '''Device group''' - to which group the device belongs (not used most of the time). | ||
* '''Type''' - what type is | * '''Type''' - what type of device it is. | ||
* '''Extension''' – short number by which this device can be reached | * '''Extension''' – a short number by which this device can be reached; must be unique in the system. | ||
* '''DTMF Mode''' – in which protocol phone button presses are sent over network | * '''DTMF Mode''' – in which protocol phone button presses are sent over network. The available options are: inband, info, RFC2833, and auto. Choose which one your provider uses (RFC2833 is used most often). | ||
* '''Works not logged''' – does user need to log | * '''Works not logged''' – does the user need to log into MOR GUI to be able to dial out? (This feature is mainly used for Call Center environments; keep the default in most cases). | ||
* '''Location''' – default Global | * '''Location''' – the default is Global. Choose the appropriate location based on [[Localization]] needs. | ||
* '''Timeout''' - how long to try to reach | * '''Timeout''' - how long to try to reach the device for, and when to hang up if the device does not answer. | ||
* '''[[Trunks | Trunk]]''' – No/Yes/Yes with ANI – Is this device Trunk with/without ANI? | * '''[[Trunks | Trunk]]''' – No/Yes/Yes with ANI – Is this device Trunk with/without ANI? | ||
* '''[[Simultaneous call limitation | Call Limit]]''' - how many simultaneous | * '''[[Simultaneous call limitation | Call Limit]]''' - how many simultaneous calls can a user make? | ||
=Authentication= | =Authentication= | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
For all other device types: | For all other device types: | ||
* '''Username''' – username you enter in your device | * '''Username''' – username you enter in your device. | ||
* '''Password''' – password you enter in your device | * '''Password''' – password you enter in your device. | ||
* '''Authenticate by IP''' – should | * '''Authenticate by IP''' – should the device be authenticated by IP (rather than by username/password)? | ||
=CallerID= | =CallerID= | ||
CallerID | A CallerID consists of two parts: name and number. The "Number" part is transferred by default by all technologies (GSM, PSTN, SIP etc), but the "Name" part only by some. The number you see on your mobile phone when someone is calling you is the "Number" part. | ||
* '''Name''' – the "Name" part of CallerID | * '''Name''' – the "Name" part of the CallerID. | ||
* '''Number''' – the "Number" part of CallerID | * '''Number''' – the "Number" part of the CallerID. | ||
NOTE: if you leave these fields empty | NOTE: if you leave these fields empty, the user can set the CallerID by himself. Usually it is not advisable to allow the user do it on his own. | ||
* '''Number from DID''' - | * '''Number from DID''' - use the DID as the CallerID (only available when the device has DIDs). | ||
* '''CID control by DIDs''' – only available when | * '''CID control by DIDs''' – only available when the device has DIDs. | ||
This setting | This setting lets you control what a CID user can enter in his devices. CID numbers should be from the set of the device's DIDs. They are mainly used when the user's PBX is connected over Trunk and many DIDs are routed to this Trunk. Calls coming out from this PBX must have a CallerID Number from the set of DIDs assigned to this Trunk (PBX). If "CID from DIDs" is checked, the system checks whether the device's CID number is from DIDs assigned to this device. If no DIDs are assigned, this value is ignored. In order for this setting to be active, CID Name/Number fields must be empty to allow the user to enter any CID number he wants. If "CID from DIDs" is checked and user enters any CID (not from his DIDs), the system will change his CID by his first available DID (selected from database by lowest ID). | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
=Network Related= | =Network Related= | ||
* '''Host''' – device IP or hostname | * '''Host''' – the device IP or hostname; the value can be "dynamic", which means that device should register (it should be like this most of the time). | ||
* '''IP Address''' - should be | * '''IP Address''' - should be the device's IP, or disabled if the device is "dynamic". | ||
* '''Port''' – port used to connect to device ( | * '''Port''' – the port used to connect to the device (the defaults are 5060 for SIP, and 4569 for IAX2). If host = dynamic, this field is updated by Asterisk when the device registers. It is the port from where the call is coming (from the device). | ||
* '''Last time registered''' - when device was last time registered to the Asterisk server | * '''Last time registered''' - when device was last time registered to the Asterisk server | ||
* '''Media control''' – | * '''Media control''' – can reinvite/transfer. Do you want your server to stay in media path between your clients and your provider | ||
* '''NAT''' – available options: yes, no, never, route. For detailed explanation | * '''NAT''' – the available options are: yes, no, never, route. For a detailed explanation of these settings, refer to [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+sip+nat here]. | ||
* '''Qualify''' – how often "ask" device about availability. More details [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+sip+qualify here] for SIP devices and [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+iax+qualify here] for IAX2 devices. | * '''Qualify''' – how often to "ask" the device about availability. More details [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+sip+qualify here] for SIP devices and [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+iax+qualify here] for IAX2 devices. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
=Groups= | =Groups= | ||
* [[What are callgroups and pickupgroups | Call Group]] – to which Call Group this device belongs | * [[What are callgroups and pickupgroups | Call Group]] – to which Call Group this device belongs. | ||
* [[What are callgroups and pickupgroups | Pickup Group]] – which | * [[What are callgroups and pickupgroups | Pickup Group]] – which Call Groups this device can pick up. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
=Voicemail= | =Voicemail= | ||
* '''Email''' – to | * '''Email''' – where to send received Voicemail. | ||
* '''Password''' – | * '''Password''' – the digital password the user enters when he calls the Voicemail number to hear his messages. | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
NOTES: | NOTES: | ||
* When no fields are checked | * When no fields are checked, all codecs are available - for example, settings in sip.conf or iax.conf are effective. | ||
* If Provider and Device | * If the Provider and the Device do not have similar codecs, no call can be established. | ||
=Allowed Addresses= | =Allowed Addresses= | ||
'''IP, MASK''' – permit traffic from | '''IP, MASK''' – permit traffic from ths IP only. You can find a detailed explanation [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/index.php?page=Asterisk+sip+permit-deny-mask here]. | ||
If you do not clearly understand | If you do not clearly understand what these settings are used for, leave them with default values. | ||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
=Advanced= | =Advanced= | ||
* '''Fromuser/Fromdomain''' – | * '''Fromuser/Fromdomain''' – used when calling TO this peer FROM Asterisk. If you're using _register=>_ with another SIP proxy, this setting can come in handy since some SIP networks only allow users in the right domain with the correct user name. | ||
* '''Trustrpid''' – | * '''Trustrpid''' – defines whether or not Remote-Party-ID is trusted. It's defined in http://tools.ietf.org/id/draft-ietf-sip-privacy-04.txt. | ||
* '''Sendrpid''' – | * '''Sendrpid''' – defines whether a Remote-Party-ID SIP header should be sent. The default setting is "no". This field is often used by wholesale VoIP providers to provide calling party identity regardless of the privacy settings (the From SIP header). | ||
* [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/index.php?page=Asterisk+sip+insecure Insecure] | * [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/index.php?page=Asterisk+sip+insecure Insecure] | ||
** port: ignore the port number where request came from | ** port: ignore the port number where request came from. | ||
** invite: don't require authentication of incoming INVITEs | ** invite: don't require authentication of incoming INVITEs. | ||
** port,invite: don't require initial INVITE to authenticate and ignore the port where the request came from | ** port, invite: don't require initial INVITE to authenticate and ignore the port where the request came from. | ||
* '''T.38 support''' - [[Fax over VoIP | Asterisk does not have good T.38 support]] so use this option just for testing | * '''T.38 support''' - [[Fax over VoIP | Asterisk does not have good T.38 support]], so use this option just for testing. | ||
* '''SIP 302 Reinvite support''' - SIP Reinvite support for device | * '''SIP 302 Reinvite support''' - SIP Reinvite support for the device. Disabled by default. | ||
* '''[http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/index.php?page=Asterisk+sip+progressinband Progressinband]''': | * '''[http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/index.php?page=Asterisk+sip+progressinband Progressinband]''': | ||
** yes - | ** yes - when "RING" event is requested, always send 180 Ringing (if it hasn't been sent yet) followed by 183 Session Progress and in-band audio. | ||
** no - | ** no - send 180 Ringing if 183 has not yet been sent, establishing an audio path. If the audio path is established already (with 183), then send in-band ringing (this is the way Asterisk historically behaved because of buggy phones like Polycom's). | ||
** never - | ** never - whenever ringing occurs, send "180 ringing" as long as "200 OK" has not yet been sent. This is the default behaviour of Asterisk. | ||
* '''Video support''' – does your provider support Video over IP? More info [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+video here]. | * '''Video support''' – does your provider support Video over IP? More info [http://www.voip-info.org/wiki/view/Asterisk+video here]. | ||
* '''[[Duplicate call prevention | Allow duplicate calls]]''' - default no | * '''[[Duplicate call prevention | Allow duplicate calls]]''' - the default setting is "no". | ||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
=Tell Options= | =Tell Options= | ||
* '''Tell balance''' – should MOR tell balance | * '''Tell balance''' – should MOR tell the user his balance every time he tries to dial? The default setting is "no". | ||
* '''Tell time''' - should MOR tell remaining time | * '''Tell time''' - should MOR tell the user his remaining time every time he tries to dial? The default setting is "no". | ||
* '''Tell remaining time when left''' – when some time is left MOR will tell remaining time to talk (in seconds) | * '''Tell remaining time when left''' – when some time is left, MOR will tell the remaining time to talk (in seconds). | ||
* '''Repeat remaining time when left''' – repeats remaining time when | * '''Repeat remaining time when left''' – repeats the remaining time when some time is left (in seconds). | ||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
=Debug= | =Debug= | ||
[[SIP debug info]] - | [[SIP debug info]] - can be enabled per SIP device basis. It is useful in debugging. When this feature is enabled, the info is saved to the calls table. | ||
Revision as of 02:58, 9 May 2010
Screenshot
Each device can have many settings. The screenshot shows settings for an SIP device. These settings are similar to those for other device types also.
There are several groups of settings: General, Authentication, CallerID, Network Related, Groups, Voicemail, Codecs, Allowed Addresses, Advanced, Tell Options, Debug and Recordings.
General
- Accountcode – the unique ID of the device in the system.
- Description – for informational purposes.
- PIN – device PIN for authentication/authorization.
- Device group - to which group the device belongs (not used most of the time).
- Type - what type of device it is.
- Extension – a short number by which this device can be reached; must be unique in the system.
- DTMF Mode – in which protocol phone button presses are sent over network. The available options are: inband, info, RFC2833, and auto. Choose which one your provider uses (RFC2833 is used most often).
- Works not logged – does the user need to log into MOR GUI to be able to dial out? (This feature is mainly used for Call Center environments; keep the default in most cases).
- Location – the default is Global. Choose the appropriate location based on Localization needs.
- Timeout - how long to try to reach the device for, and when to hang up if the device does not answer.
- Trunk – No/Yes/Yes with ANI – Is this device Trunk with/without ANI?
- Call Limit - how many simultaneous calls can a user make?
Authentication
For ZAP devices:
- Channel – which channel (or channel group) to use on PRI/BRI/PSTN card. Channels and groups should be configured in zapata.conf.
For all other device types:
- Username – username you enter in your device.
- Password – password you enter in your device.
- Authenticate by IP – should the device be authenticated by IP (rather than by username/password)?
CallerID
A CallerID consists of two parts: name and number. The "Number" part is transferred by default by all technologies (GSM, PSTN, SIP etc), but the "Name" part only by some. The number you see on your mobile phone when someone is calling you is the "Number" part.
- Name – the "Name" part of the CallerID.
- Number – the "Number" part of the CallerID.
NOTE: if you leave these fields empty, the user can set the CallerID by himself. Usually it is not advisable to allow the user do it on his own.
- Number from DID - use the DID as the CallerID (only available when the device has DIDs).
- CID control by DIDs – only available when the device has DIDs.
This setting lets you control what a CID user can enter in his devices. CID numbers should be from the set of the device's DIDs. They are mainly used when the user's PBX is connected over Trunk and many DIDs are routed to this Trunk. Calls coming out from this PBX must have a CallerID Number from the set of DIDs assigned to this Trunk (PBX). If "CID from DIDs" is checked, the system checks whether the device's CID number is from DIDs assigned to this device. If no DIDs are assigned, this value is ignored. In order for this setting to be active, CID Name/Number fields must be empty to allow the user to enter any CID number he wants. If "CID from DIDs" is checked and user enters any CID (not from his DIDs), the system will change his CID by his first available DID (selected from database by lowest ID).
Network Related
- Host – the device IP or hostname; the value can be "dynamic", which means that device should register (it should be like this most of the time).
- IP Address - should be the device's IP, or disabled if the device is "dynamic".
- Port – the port used to connect to the device (the defaults are 5060 for SIP, and 4569 for IAX2). If host = dynamic, this field is updated by Asterisk when the device registers. It is the port from where the call is coming (from the device).
- Last time registered - when device was last time registered to the Asterisk server
- Media control – can reinvite/transfer. Do you want your server to stay in media path between your clients and your provider
- NAT – the available options are: yes, no, never, route. For a detailed explanation of these settings, refer to here.
- Qualify – how often to "ask" the device about availability. More details here for SIP devices and here for IAX2 devices.
Groups
- Call Group – to which Call Group this device belongs.
- Pickup Group – which Call Groups this device can pick up.
Voicemail
- Email – where to send received Voicemail.
- Password – the digital password the user enters when he calls the Voicemail number to hear his messages.
Codecs
Choose the codecs your provider uses.
NOTES:
- When no fields are checked, all codecs are available - for example, settings in sip.conf or iax.conf are effective.
- If the Provider and the Device do not have similar codecs, no call can be established.
Allowed Addresses
IP, MASK – permit traffic from ths IP only. You can find a detailed explanation here.
If you do not clearly understand what these settings are used for, leave them with default values.
Advanced
- Fromuser/Fromdomain – used when calling TO this peer FROM Asterisk. If you're using _register=>_ with another SIP proxy, this setting can come in handy since some SIP networks only allow users in the right domain with the correct user name.
- Trustrpid – defines whether or not Remote-Party-ID is trusted. It's defined in http://tools.ietf.org/id/draft-ietf-sip-privacy-04.txt.
- Sendrpid – defines whether a Remote-Party-ID SIP header should be sent. The default setting is "no". This field is often used by wholesale VoIP providers to provide calling party identity regardless of the privacy settings (the From SIP header).
- Insecure
- port: ignore the port number where request came from.
- invite: don't require authentication of incoming INVITEs.
- port, invite: don't require initial INVITE to authenticate and ignore the port where the request came from.
- T.38 support - Asterisk does not have good T.38 support, so use this option just for testing.
- SIP 302 Reinvite support - SIP Reinvite support for the device. Disabled by default.
- Progressinband:
- yes - when "RING" event is requested, always send 180 Ringing (if it hasn't been sent yet) followed by 183 Session Progress and in-band audio.
- no - send 180 Ringing if 183 has not yet been sent, establishing an audio path. If the audio path is established already (with 183), then send in-band ringing (this is the way Asterisk historically behaved because of buggy phones like Polycom's).
- never - whenever ringing occurs, send "180 ringing" as long as "200 OK" has not yet been sent. This is the default behaviour of Asterisk.
- Video support – does your provider support Video over IP? More info here.
- Allow duplicate calls - the default setting is "no".
Tell Options
- Tell balance – should MOR tell the user his balance every time he tries to dial? The default setting is "no".
- Tell time - should MOR tell the user his remaining time every time he tries to dial? The default setting is "no".
- Tell remaining time when left – when some time is left, MOR will tell the remaining time to talk (in seconds).
- Repeat remaining time when left – repeats the remaining time when some time is left (in seconds).
Debug
SIP debug info - can be enabled per SIP device basis. It is useful in debugging. When this feature is enabled, the info is saved to the calls table.
Recordings
This section is available when Recordings Addon is installed in the system.